Radon is a radioactive gas that silently infiltrates homes, posing a significant health risk. When high radon levels are detected in a home a radon mitigation system if often installed to reduce the levels and ensure the safety of those living there. In this article, we will explore the current costs of these systems and why investing in them is essential for safeguarding your health. As of October 2023, the cost of a radon mitigation system can vary depending on several factors, such as the size of the home, the type of system, and the location. The average cost of a radon mitigation system is around $1,000, according to Forbes, HomeAdvisor, and National Radon Defense. However, the cost can range from $700 to $4,000. Why pay that much? Well, long-term exposure to radon gas is the leading cause of lung cancer behind smoking, killing around 21,000 Americans each year according to the EPA. So a functioning radon mitigation system can help protect you from exposure to elevated levels of radon gas.
How do I know I need a radon mitigation system?
If you haven't tested your home for radon yet, you should do so before investing in a radon mitigation system. Consumer-grade electronic radon monitors like the Corentium Home, View Radon, or View Plus are relatively affordable, with prices ranging from $120 to $300. These products last for years and can give you long-term peace of mind about the air you breathe at home. Compared to the potential health risks and costs associated with long-term radon exposure and the costs of installing a radon mitigation system without a radon problem, investing in a radon monitor even with a radon mitigation system is a cost-effective solution to ensure the problem is tackled 100% and that your mitigation system keeps working.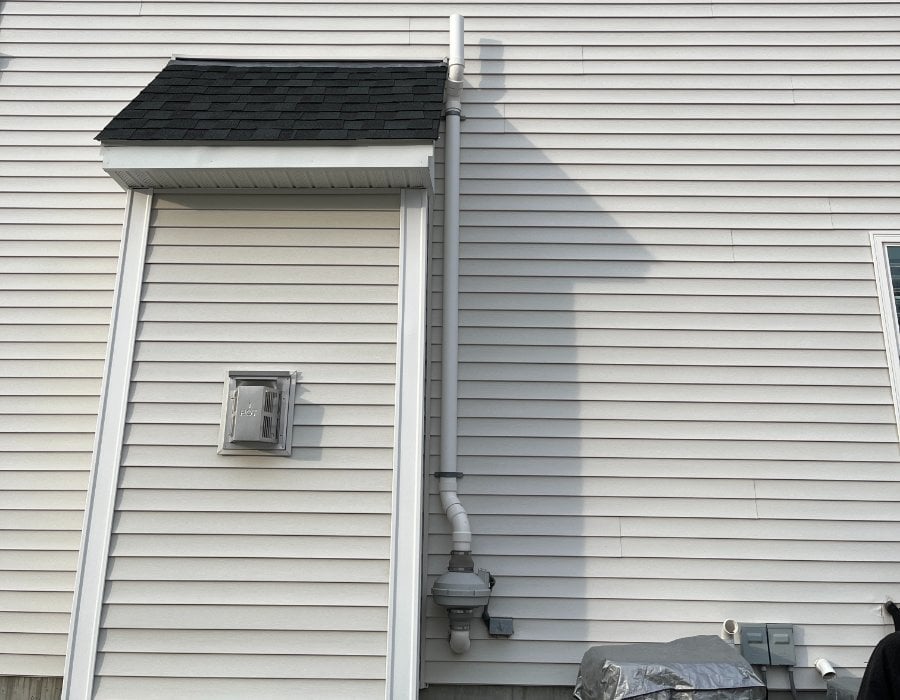 
The purpose of a radon mitigation system
A radon mitigation system, also known as a radon reduction system, actively removes radon gas from your home, safeguarding you and your family from its harmful effects. This is achieved by extracting radon gas from below the building and expelling it above and away from the structure. Radon mitigation not only removes radon from breathable air but can also address radon in drinking water.
As previously stated, before installing a radon system, your home should be tested for radon content to avoid fixing a problem that isn't there. An "actionable level" of radon is the threshold at which it is recommended to seek a radon mitigation system. The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) suggests an action level of 4.0 pCi/L (picocuries per liter), while the World Health Organization's international recommended maximum is 2.7 pCi/L. .png) Airthings app with Radon graphs. Product placement: View Plus in the living room, View Radon in the basement.
Airthings app with Radon graphs. Product placement: View Plus in the living room, View Radon in the basement.
Factors to consider when installing a radon mitigation system
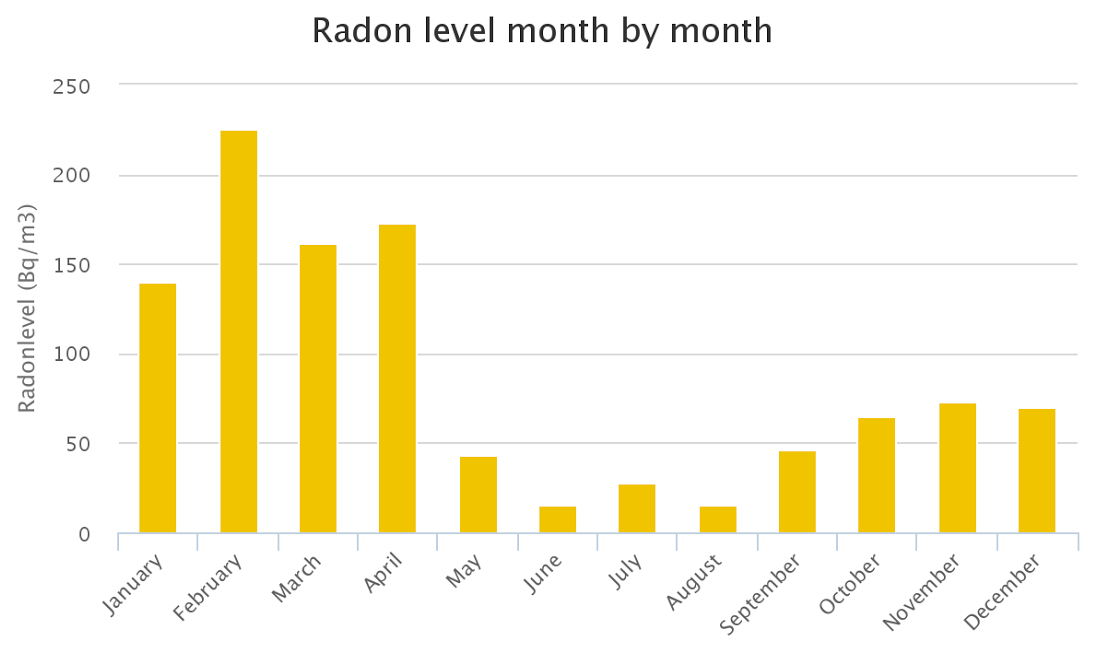
Various factors affect radon levels in your home, including seasonal variations. Radon levels may differ between summer and winter due to the nature of the gas. This fluctuation underscores the importance of long-term monitoring rather than relying solely on short-term tests.
Short-term radon test kits can provide quick assessments of radon levels but may require sending samples to a lab for analysis. Long-term detectors actively gauge radon levels and provide readings within hours. It is advisable to conduct multiple tests to ensure accuracy.
How does a radon system work?
Radon mitigation primarily employs a suction and piping system to draw air from beneath a home and expel it safely outdoors. This process, known as "sub-slab depressurization" or "soil suction," creates negative pressure beneath the house, diverting radon-laden air away from living spaces. These systems can be adapted for crawl spaces and basements, depending on your home's construction.
While it might seem intuitive to address radon by increasing airflow, doing so without a properly sealed system can actually exacerbate the issue. Opening windows can bring more radon into your home rather than eliminating it. A well-designed radon system effectively diverts radon away from your home.
The lifespan of radon mitigation systems
The lifespan of radon mitigation systems varies, but proper maintenance, installation quality, and the type of system used are crucial factors. While some components like PVC piping can last a long time, radon fans may need replacement after a few years. Regular maintenance can extend the system's lifespan, and retesting for radon every two years is recommended. Next is, radon fluctuates, therefore there is a high chance that when the radon mitigation system was put in place the spread of radon gas was not at its peak, investing in long-term monitoring would help tackle and improve the radon mitigation system to eliminate risks in both in peaking and low radon seasons.
Why install a radon mitigation system?
- Health Benefits: The primary advantage of radon mitigation systems is their potential to reduce radon concentrations, thereby lowering the risk of lung cancer.
- Safety: These systems transform radon-contaminated homes into safe living environments, ensuring the well-being of occupants.
- Proven Effectiveness: Radon reduction systems can reduce radon levels by up to 99%, a statistic supported by numerous studies collected by University of Nevada.
- Tailored Solutions: Radon mitigation systems can be customized to suit the unique conditions of each building, ensuring their efficacy.
How to validate if a radon mitigation was effective
To ensure your radon mitigation system is working effectively, follow these steps:
- Monitor radon levels short-term and long-term: After system installation, retest your home to confirm radon reduction. Keep an eye on your system for the whole year after mitigation takes place.
- Maintain the System: Regular maintenance, including fan cleaning and inspection, can extend the system's lifespan. Professional inspections are recommended every one to two years depending on the radon levels.
- Check for other sources of radon: Address potential radon sources, such as well water or building materials, to supplement mitigation efforts.
- Consult a Professional: If in doubt, consult a professional radon contractor to inspect your system and provide guidance.
.png)
No radon mitigation system can guarantee a complete reduction to zero, but a well-designed, properly installed system can significantly reduce radon levels, minimizing health risks.
In summary, radon mitigation systems play a crucial role in safeguarding your health by effectively reducing radon concentrations. While the cost may vary, it adds value to your home and provides peace of mind, knowing you're taking steps to protect your long-term health.
FAQ
What is the success rate of radon mitigation?
Radon reduction system works, however, requires continuous monitoring. An efficient radon mitigation system will help you reduce your radon levels from 94 percent to 97 percent.
Who can help me install a radon mitigation system?
A professional radon mitigator can help you reduce elevated radon gas levels in buildings using techniques such as sub-slab depressurization, ventilation systems, and sealing openings. Search local directories, contact state radon programs, or use online platforms to find a certified radon mitigator in your area.
What causes radon in home?
Radons are radioactive gases. It is derived from the decay of uranium found in almost all soils. In most cases, it is able to pass through a crack or other hole in your foundation and enter your residence. Your house contains radon which accumulates inside the building.
What is a dangerous radon level?
The EPA recommends homes be fixed if the radon level is 4 pCi/L or more, and also recommends considering fixing their home for radon levels between 2 pCi/L and 4 pCi/L
Sources:
https://www.forbes.com/home-improvement/home/radon-mitigation-system-cost-guide/
https://www.homeadvisor.com/cost/environmental-safety/remove-radon-gas/
https://www.nationalradondefense.com/about-us/articles/43211-radon-mitigation-system-cost.html
https://www.epa.gov/radon/health-risk-radon
https://www.epa.gov/radon/what-epas-action-level-radon-and-what-does-it-mean
https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/radon-and-health
https://extension.unr.edu/publication.aspx?PubID=2706