Radon is a radioactive gas that is colorless, odorless, and tasteless making it impossible to detect without a device.Moreover, it is recognized as the leading cause of lung cancer among non-smokers by the EPA. Hence, early detection is key to improve your long-term health. As the market is flooded with products for radon detection, the question is: what type of radon detection system should you get?
Different radon detection methods
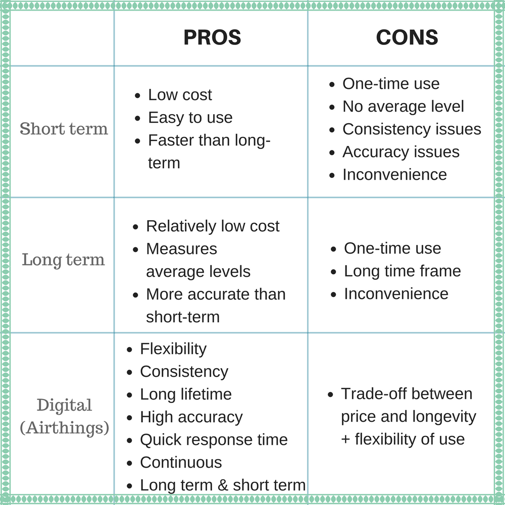
The type of radon detection system you should purchase depends on the purpose, the desired speed of results, and accuracy. To simplify, radon detection has historically been separated into short-term and long-term tests according to Oregon Public Health. However, with more advanced technology, digital solutions have made testing for radon more convenient and accurate.
Short-term radon detection
Short-term radon detection is suitable if you need a speedy answer that will take between 2 days and 3 months. For instance, you can use it after buying a house to check if you need radon mitigation work. These types use charcoal based methods to absorb the radon gas which is later resealed and returned to the vendor or lab for evaluation.
The main advantage of this is speed as it takes less than 90 days for the results which make it significantly faster than long-term methods. However, it still takes a long time to get the results back from the lab. These kits are also cheap and can cost anything from $10 to $30 per kit. The problem (as mentioned in an earlier post) is that they are unreliable due to the vulnerability for errors. For instance, different temperatures and humidity levels might cause sensitivity issues within the products. Furthermore, it does not give an average radon level which makes it less accurate due to the fluctuating levels of radon throughout the year(s) (illustrated in the image below).
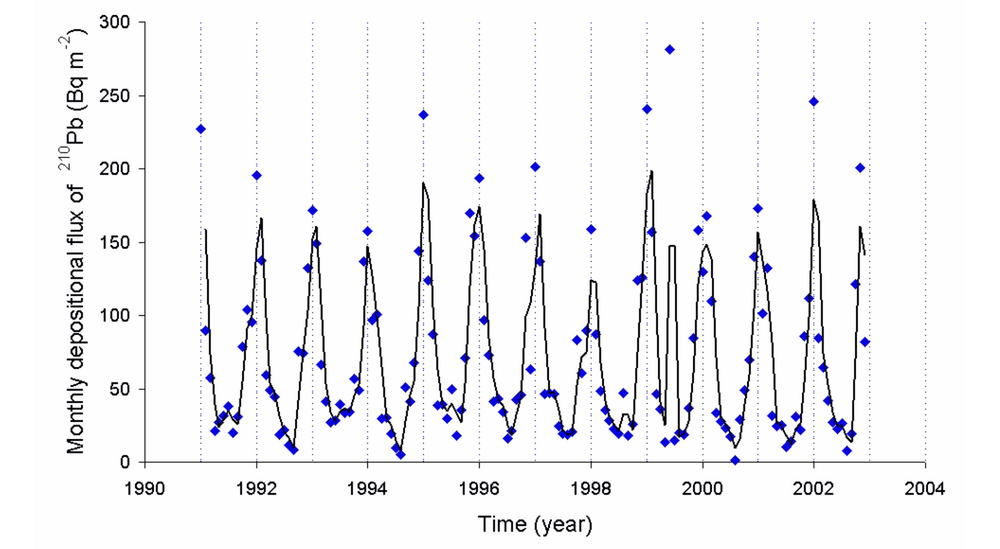
Long-term radon detection
As mentioned by Oregon Public Health, these radon detectors are usually based on Alpha-Track Detection (AT) method. They use containers that enclose small sheets of special plastic material to detect radiation. In short, the alpha particles emitted by the radon gas will leave tracks on these plastic sheets for later evaluation. This process may take anything from 3 months up to a year depending on the product.
Since these methods are used for the long-term, it provides more accurate readings than the short-term methods as it measures the average radon levels. However, the accuracy varies from product to product. The problem with these products is also the length of time it takes to get the results. Furthermore, similar to short-term methods, it is also inconvenient as you need to return items for processing and evaluation.
Digital solutions: the future of radon detection

Although the "old school" methods of radon detection have worked in the past, the hassle of returning items to the vendor takes both time and effort. In other words, it becomes less convenient to measure radon. By digitalizing radon detection, Airthings have created a solution that combines the advantages of these methods while making it more convenient for the end user.
The advantage here is that you can use these products for both short-term and long-term measurement purposes. If you are looking for short-term solutions, you can get an answer with Airthings Wave within 2 hours or within 24 hours for Home. Moreover, for long-term purposes, it can measure radon levels continuously thereby giving you up-to-date results so that fluctuating radon levels do not become a problem. There is also a wide range of products giving you the flexibility of choice. For instance, if you would like to measure radon levels in each room you can use products such as Home. Although these types of products tend to be somewhat pricey, they are designed to last up to 10 years. In other words, there is a trade-off between the price (equivalent to around 8 long-term test kits) and all the benefits listed in the diagram below.
In a nutshell: Pros & cons of radon detection systems
What should I do if radon levels are too high?
Once you have found the right type of radon detection system for your purpose, the next logical question is: what is an acceptable range and what should you do if they are too high? More information about radon levels and how to respond can be found here.
Sources
- Alvarez, J. L. (1990). "Analytic Procedures and Comparisons". Radon.com. Accessed from: www.radon.com. Retrieved 14 June 2017
- EPA (n.d.). "Health Risk of Radon". EPA.gov. Accessed from: www.epa.gov. Retrieved 14 June 2017.
- Kristiansen, C. (2017). "Charcoal Versus Airthings – Accuracy". Airthings.com. Accessed from: www.airthings.com. Retrieved 14 June 2017.
- Kristiansen, C. (2017). "How to respond to your radon levels". Airthings.com. Accessed from: www.airthings.com. Retrieved 14 June 2017.
- Oregon Public Health (n.d.) "Type of Radon Gas testing". Oregon.gov. Accessed from: public.health.oregon.gov. Retrieved 14 June 2017.












%20(1).webp)

%20(1).webp)
