Good indoor air quality directly affects the health and comfort of building occupants. Understanding and controlling common contaminants indoors can help reduce your risk of air quality health concerns. Contaminants or pollutants cause the air you breathe to become unhealthy. Ventilation, inhabitants, use of space and household items all contribute to indoor air quality.

Decrease exposure to this odorless, radioactive gas found in all buildings and homes. It is the number one cause of lung cancer amongst non-smokers but can be managed with long-term, continuous monitoring.
Particulate matter, or PM, isn’t just one contaminant or pollutant. It’s a range of particles of dust, dirt, and liquids that become suspended in the air. Find out the difference between PM1, PM2.5 and PM10 today.
TVOCs are odors and chemicals emitted from many everyday products, including cleaners, paints and furniture, cosmetics, hobby products, cooking and even human breath.
CO2 is an invisible gas that comes from human breath. It can cause headaches, restlessness and drowsiness as well as affect decision-making skills. High levels are correlated to low productivity, absenteeism and infectious disease transmission.

Approximately 21,000 people in the US and 20,000 in the EU die from radon-related lung cancer every year.

Studies have found that levels of VOCs or airborne chemicals average 2 to 5 times higher indoors than outdoors.

An increase of 400ppm in CO2 caused cognitive function to decline by 21%, seriously impairing judgment and decision-making.
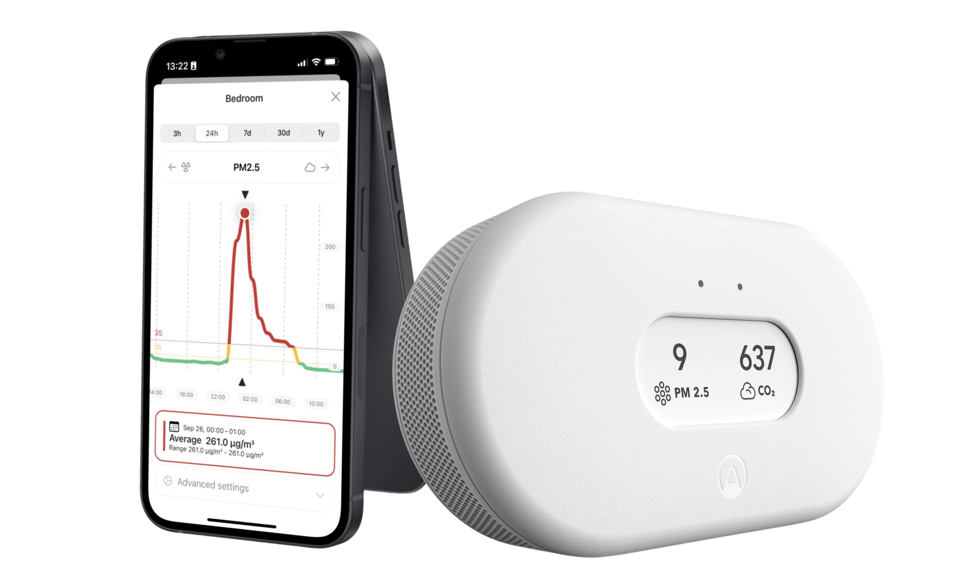
Making small changes to your every day habits can make a big impact on the health of your air. Take control of the air you breathe by monitoring indoor air quality in homes, schools, offices, and all other indoor spaces.